Most people may be familiar with COB LED displays, but may not know about the latest pixel protection technology—GOB LED displays. This article will explore how GOB (on-board adhesive) helps protect LED displays.
What is GOB?
To understand HOB (HOB/HGOB), we first need to understand what GOB is.
On-board adhesive, or GOB for short, is an epoxy resin coated onto the surface of a surface-mount display module (SMD) to form an adhesive layer, thereby improving the sealing of the SMD display. This technology aims to solve the problem of LED chip protection. GOB LED displays can operate in various harsh environments, featuring waterproof, dustproof, shockproof, and UV-resistant properties, and are widely used in restaurants, hotels, bars, and sports venues.
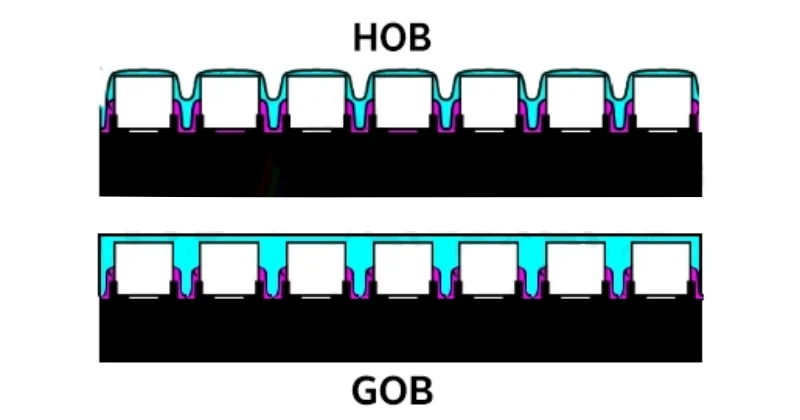
What is HOB?
The HOB (on-board hot melt adhesive) process uses high-refractive-index nanomaterials to coat the screen surface, forming a protective layer that completely covers the LED chips. This protective layer prevents the LED chips from being affected by external factors, improving their stability and lifespan. Furthermore, it can improve the quality and efficiency of the LED display during the encapsulation process.
HOB uses a high-temperature molding process, while GOB uses a room-temperature dispensing process. HOB is superior to GOB in terms of thermal stability, precision, flatness, and thickness control. Furthermore, the high-temperature molding process prevents the adhesive layer from cracking due to heat during LED operation.

Durability
HOB uses a COB process, employing a polymer synthetic colloid containing various additives, coagulants, and UV stabilizers for high-temperature molding. This not only prevents the yellowing problem of ordinary epoxy resins but also allows for adjustment of the amount of black pigment and the design of a frosted mold surface.
Scratch Resistance
Place traditional GOB products and HOB products side-by-side and scratch their surfaces with a screwdriver; you will see a clear difference. GOB products are not scratch-resistant, immediately showing scratches and cracks, while HOB products remain intact. This is because HOB products use the COB process, employing a high-temperature polymer synthetic colloid for injection molding, which includes various additives, coagulants, and UV stabilizers. This not only avoids the yellowing problem of ordinary epoxy resin but also allows for the modification of black pigments to create a frosted surface on the mold.

Optical Performance
The GOB process results in uneven thickness and variations in the flatness of the self-leveling colloid, leading to a thicker GOB product. This causes more noticeable edge refraction issues, commonly known as “bright lines,” when splicing large areas.
HCOB uses precision molds to ensure its thickness is only 0.2mm higher than the LED height, and light experiences almost no secondary refraction at the colloid edges.
Contrast Ratio
The final product of the ordinary GOB process has a mirror-like surface, making it impossible to achieve a frosted or matte effect.
HCOB uses mold design and pressure molding processes to create a matte black-like frosted surface, improving the overall screen contrast ratio by 40%.

HCOB uses high-precision mold technology to control the overall molding precision within 0.2mm (based on traditional mold precision). GOB uses a room temperature molding process, relying on internal molecular solidification, which results in shrinkage issues. Currently, the optimal precision of GOB is 0.5mm, and some products require secondary processing. HCOB technology has been applied in batches to the mainstream pitches of 1.2, 1.5, and 1.8mm.
